What Causes Cellulitis?
Cellulitis is a common skin infection that can be both painful and serious.
It is caused primarily by bacteria, such as Streptococcus and Staphylococcus, entering the skin through cuts or wounds.
Factors that may make you susceptible to cellulitis include:
- Weakened immune system
- Recent skin injuries, such as scrapes, cuts, or an insect bite
- Poor circulation
- Exposure to particular bodies of water
- Chronic conditions, such as lymphedema or diabetes
Understanding what leads to cellulitis can help you prevent and manage this condition, which most commonly occurs on the lower legs, where the skin is more prone to damage.
Conditions like athlete’s foot or dermatitis can create openings for bacteria to invade.
What are the early signs of cellulitis?
Early symptoms of cellulitis include redness, swelling, and warmth in the affected area.
Recognizing these risks is key to protecting yourself and seeking timely treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Cellulitis is caused by bacteria entering broken skin.
- It often appears on the lower legs but can occur elsewhere.
- Insect or animal bites, puncture wounds, and water exposure can also lead to cellulitis.
What is Cellulitis?
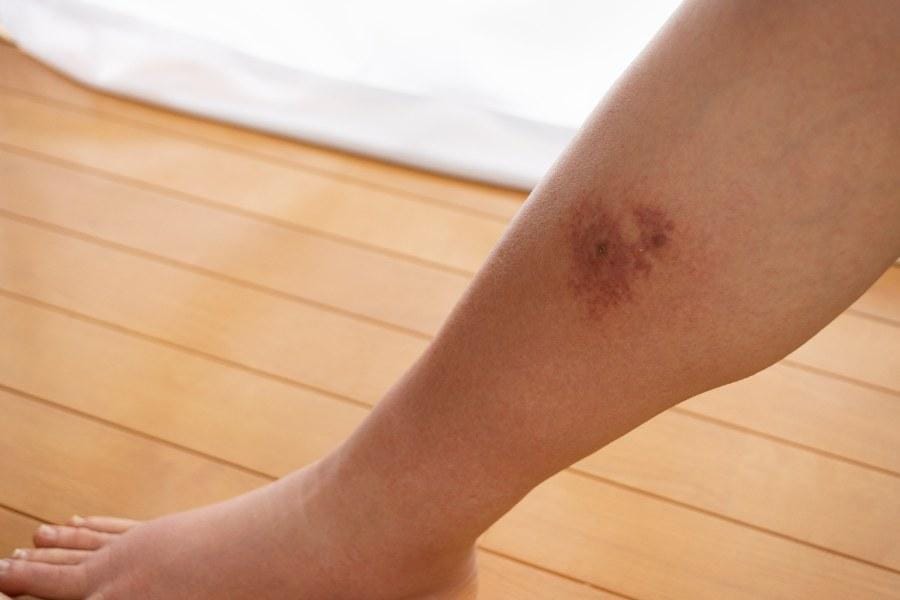
Cellulitis is a common bacterial skin infection. It often results in redness, swelling, and warmth in the affected area.
By exploring its definition and comparing cellulitis to similar conditions, you can gain a clearer understanding of this medical issue.
Definition and Overview of Cellulitis
Cellulitis is a bacterial infection that affects the skin and soft tissues beneath it. It is commonly caused by bacteria like Streptococcus and Staphylococcus entering through cuts or breaks in the skin.
Symptoms typically include redness, warmth, and swelling, and the area may be tender or painful.
Cellulitis can be serious if not treated promptly, sometimes leading to fever and feeling unwell. Unlike cellulite, which is a cosmetic skin condition resulting from fat deposits under the skin, cellulitis is a medical concern that requires attention.
Early treatment usually involves antibiotics, and most cases resolve without complications if caught early. It is crucial to monitor any such symptoms and consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Comparison to Similar Conditions
Cellulitis is often confused with other skin infections or conditions because of similar symptoms.
For example, athlete’s foot and eczema can cause redness and swelling but are not caused by bacterial infections.
Erysipelas is another condition similar to cellulitis, but it mostly affects the upper layers of the skin and shows a well-defined edge that distinguishes it.
Unlike cellulitis, superficial skin infections do not penetrate deep into the skin tissues and might not require aggressive treatments.
Recognizing these differences is vital for correct treatment and effective recovery. For more detailed comparisons between cellulitis and other skin issues, check sources like the Mayo Clinic.
Causes and Risk Factors of Cellulitis
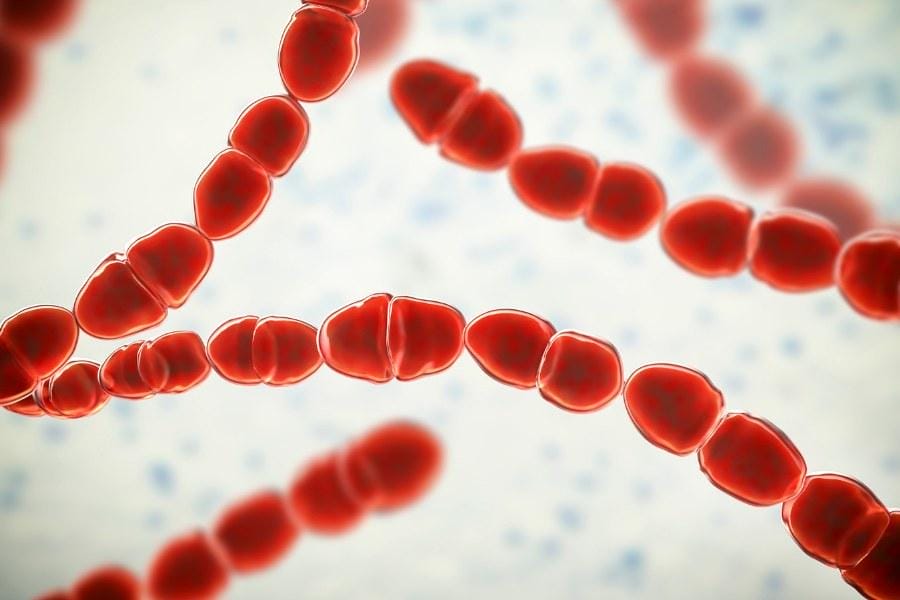
As we have stated, cellulitis is often caused by bacteria entering through a break in the skin.
Understanding which bacteria are most common and what factors increase your risk can help in prevention and management.
Common Bacteria Involved
The main culprits in cellulitis are bacteria like Streptococcus and Staphylococcus.
When these bacteria enter your skin through cuts, scrapes, or other injuries, they can cause infections.
Streptococcus is known for causing inflammation and redness, common signs of cellulitis.
On the other hand, Staphylococcus can lead to more serious infections, including bacteremia, which is a presence of bacteria in your bloodstream. It might also result in complications like osteomyelitis and endocarditis.
Regularly cleaning and treating wounds can help reduce the risk. Since both these bacteria are common, proper hygiene and care are essential in preventing their spread. In some cases, antibiotics might be necessary to tackle these bacterial infections effectively.
Factors Contributing to Susceptibility
Several conditions can increase your risk of developing cellulitis. A weakened immune system, due to illnesses like HIV/AIDS or diabetes, makes you more susceptible to infections.
Skin conditions like eczema, psoriasis, and atopic dermatitis can also serve as entry points for bacteria because they compromise the skin barrier.
Venous insufficiency, where blood doesn’t flow properly in your veins, is another risk factor. This condition can cause swelling and skin breakdown, increasing bacteria’s access.
To reduce risk, pay attention to skin health by using moisturizers and avoiding irritants that might harm the skin barrier.
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation
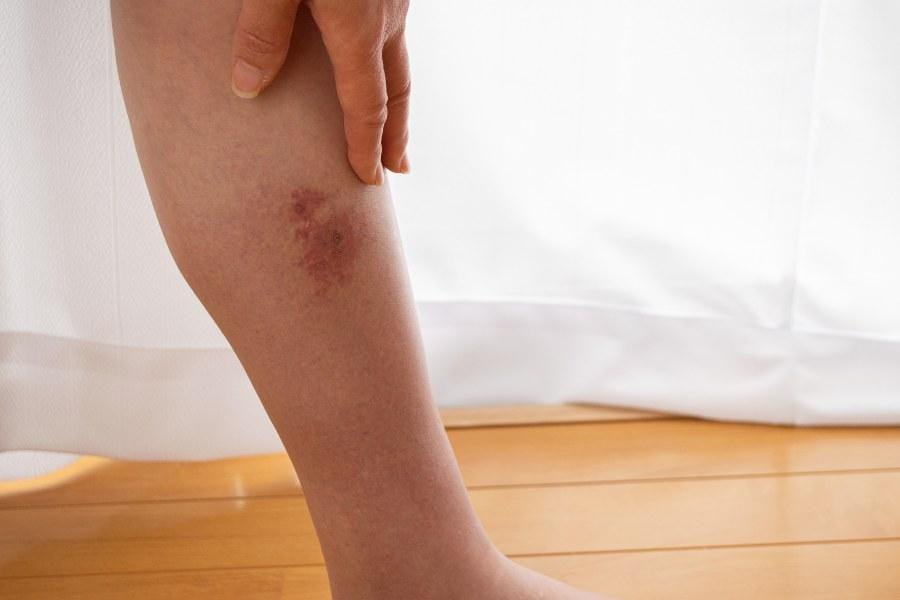
When dealing with cellulitis, it’s essential to recognize both physical and systemic manifestations.
These symptoms often help in early detection and effective treatment.
Physical Symptoms of Cellulitis
Physical signs of cellulitis are usually noticeable on the skin. You might observe redness and swelling in the affected area.
The skin often feels warm and may be tender to touch. A rash or discolored patches can develop as well.
It’s common for the area to appear shiny due to stretched skin. Blisters or small sores might also form. These symptoms can make the skin feel painful, especially if pressure is applied.
In some cases, the infection causes swollen skin, signaling fluid accumulation or edema. This symptom is crucial for identifying cellulitis, especially when coupled with other visible changes.
Systemic Effects and Complications
The systemic effects of cellulitis can extend beyond the local skin symptoms.
You may experience fever, chills, and fatigue. These symptoms resemble flu-like conditions, often making it challenging to perform daily activities.
Infections can escalate if untreated, leading to severe complications like lymphedema.
This involves long-term swelling due to the lymphatic system being affected.
Your body might also develop more serious issues, such as bloodstream infections if cellulitis spreads. Seeking timely medical advice is crucial to prevent these potential complications from escalating further.
Cellulitis Diagnostic Approaches
Identifying cellulitis involves a careful assessment of symptoms and medical history.
Techniques range from physical exams to laboratory tests, ensuring a comprehensive diagnosis and prompt medical care.
Physical Examination
During a physical examination, your doctor will look closely at the affected skin area.
They check for redness, warmth, swelling, and tenderness. Feeling the skin might reveal changes in texture or temperature.
The lymph nodes near the infection site are also examined, as swelling here can indicate how far the infection has spread.
Your doctor will also inquire about any recent injuries or processes that could allow bacteria to enter the bloodstream.
This examination helps rule out other conditions like eczema or contact dermatitis, which might mimic cellulitis symptoms.
Laboratory Tests and Imaging
In some cases, additional tests are necessary. Blood tests can reveal signs of infection. They check for elevated white blood cell counts or other markers that signal your body is fighting an infection.
If there’s doubt about the diagnosis, other tests like imaging may be conducted.
An ultrasound or MRI can help show how deep the infection goes. These tools are especially helpful if the precise nature or extent of the infection is unclear.
They assist in distinguishing cellulitis from deeper or more chronic conditions.
Note: Laboratory tests are crucial when symptoms don’t clearly match those of cellulitis, providing more data for a precise diagnosis.
Treatment Strategies for Cellulitis
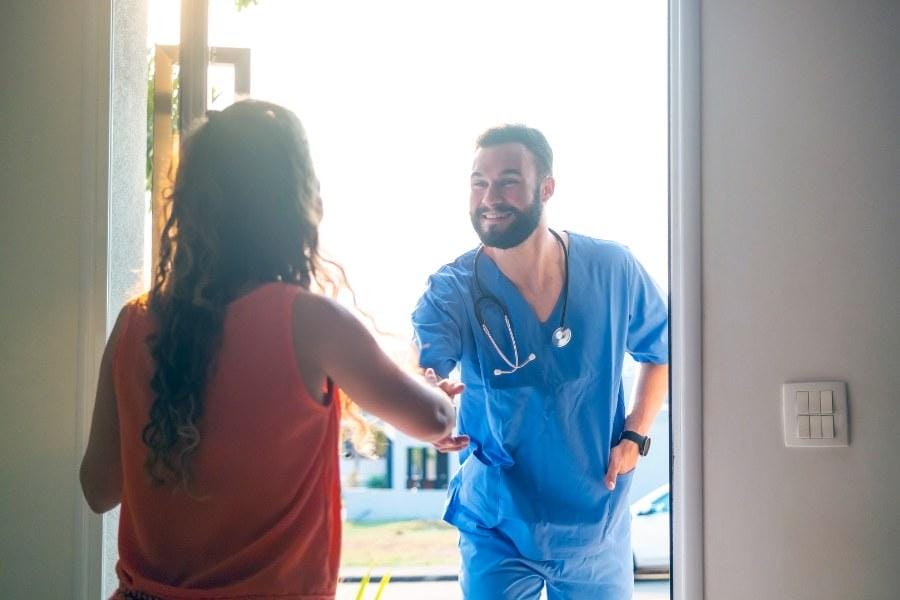

Treating cellulitis often involves antibiotics, proper wound care, and knowing when to get professional help.
These methods can help you manage the infection effectively.
Antibiotics and Drug Therapy
Cellulitis treatment typically starts with antibiotics. Most cases can be treated with an oral antibiotic that you take at home, lasting about 5 to 10 days.
You need to complete the full course of antibiotic treatment, even if you feel better early on, to ensure the infection is completely cleared.
In more severe cases, you might need intravenous antibiotics. This usually happens if the infection covers a large area or if you have underlying health issues that could complicate recovery.
It is crucial to monitor your symptoms and inform your healthcare provider if they worsen or do not improve quickly.
Home Care and Prevention
While you are going through the treatment of cellulitis, some home care can help ease symptoms. Services like home nursing care can be incredibly beneficial here.
Keep the affected area clean and elevate it to reduce swelling. Applying a cool, damp cloth might also help with discomfort.
You can prevent future episodes by practicing proper wound care. Keeping skin moisturized and wearing protective clothing can help reduce the risk of cuts and scratches.
Regularly check your skin for any signs of infection, especially if you have conditions like diabetes.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Cellulitis
While many cases improve with antibiotics, certain signs mean you should contact a doctor.
Seek medical attention if the area of redness expands, symptoms worsen, or you develop high fever or chills. If your oral antibiotics do not seem effective, it might be a sign that stronger intravenous antibiotics are necessary.
Always prioritize your health by swiftly consulting a healthcare provider for any persistent or severe symptoms.
Recognizing these signals can help avoid complications from cellulitis.
Get At-Home Nursing Care for Cellulitis
If you have recently been discharged from a hospital or treated for cellulitis and need at-home wound care, NurseRegistry is here to help.
We offer highly specialized, friendly, and professional nurses who excel at wound infection care.
Not only that, but NurseRegistry offers industry-leading scheduling flexibility. That means you will receive your wound care exactly when and where you need it from a trained medical professional rather than a caregiver.
Click below to get a private nurse for cellulitis wound care below.
People Also Ask about Cellulitis
Cellulitis is a common skin infection caused by bacteria entering the body through breaks in the skin. It can appear differently in various locations and can lead to more severe health issues if untreated. Understanding its symptoms, effects, and risks is crucial for timely intervention and treatment.
What causes cellulitis in the legs?
Cellulitis in the legs often occurs due to bacteria entering through cuts, scrapes, or other open wounds. Conditions like athlete’s foot or eczema can also create entry points for bacteria, increasing the risk of infection in the legs.
How does cellulitis affect my body?
Cellulitis leads to symptoms like redness, swelling, and pain in the affected area. It may also cause systemic symptoms such as fever, chills, and fatigue, impacting your overall well-being.
How common is cellulitis?
Cellulitis is a frequent bacterial skin infection, with cases varying in severity. It affects numerous people annually and is a common reason for hospital visits related to skin infections.
When should someone worry about cellulitis symptoms?
You should seek medical attention if you experience severe symptoms like spreading redness, fever, increasing pain, or unusual drainage. Early intervention can prevent complications.
What are the different types of cellulitis?
There are various types based on affected areas, including periorbital cellulitis around the eyes and facial cellulitis. Each type has specific symptoms and potential risks requiring different approaches to treatment.
Can cellulitis lead to sepsis and what are its symptoms?
Yes, if untreated, cellulitis can progress to sepsis, a severe body-wide reaction. Symptoms of sepsis include high fever, rapid heartbeat, confusion, and difficulty breathing. Immediate medical care is essential.
How dangerous is a cellulitis infection?
While often treatable, mild cellulitis can become dangerous if it spreads or goes untreated, leading to complications like abscesses, blood infections, or tissue damage.
Can poor hygiene contribute to the development of cellulitis?
Poor hygiene can increase the risk of cellulitis by allowing bacteria to infiltrate through skin breaches. Regular cleaning of wounds and good hygiene practices can help reduce this risk.
What does the beginning of cellulitis look like?
Early signs of cellulitis include localized redness, heat, and tenderness in the affected area. These symptoms indicate the onset of infection and demand prompt medical evaluation.
How to Prevent Cellulitis
To avoid cellulitis, practice good hygiene by keeping your skin clean and moisturized, promptly cleaning and bandaging any cuts or scrapes, wearing protective clothing and footwear to avoid injuries, and treating existing skin conditions like athlete’s foot as soon as possible; if you have a wound, avoid public swimming areas such as pools and hot tubs until it is fully healed.
The post What Causes Cellulitis? appeared first on NurseRegistry.The post What Causes Cellulitis? appeared first on NurseRegistry.
from NurseRegistry https://ift.tt/QZkeNB9

Comments
Post a Comment